Cantore Arithmetic is able to word Sequel to word Series as stated to word: Organ at the current Fibonacci sequence.
With this ratio word heaven equated conch!!
Addendum: Word same as exact to difference at Albert Einstein remains. This is division.
Addendum II Word 2024: All city and Town to village of the King on the Bobby Fischer Chess Chicanery The Mechanical Turk, also known as the Automaton Chess Player (German: Schachtürke, lit. 'chess Turk'; Hungarian as Hungarian equated Hurricane: Now, are in the Cloud(Youtube reference(GOOGLE T.V. Guide)). the efficiency quotient for City Identification is Able to rate Map on Population to square as triangle to barrow for the work and/or present in said plate as per The Weather Channel and the clouds: About 681,000 results (0.33 seconds) for the horseshoe vortices as per May 20, 2023 and Explaining How This Strange Cloud Formed: You might be wondering how something like this could even form naturally. Horseshoe vortices are quite rare; The Weather Channel. Weather Wise: Horseshoe Vortex Clouds reported by meteorologist Curtis Grevenitz 8KPAX
Addendum III: Waves equated weaves. Luke 21:25 “And there shall be signs in the sun, and in the moon, and in the stars; and upon the earth distress of nations, with perplexity; the sea and the waves roaring;” King James Version (KJV). Weaver to horse at weaves: United States Pony Club.
Genesis 1:1
“In the beginning God created the heaven and the earth.”
King James Version (KJV)
1 Peter 5:9
“Whom resist stedfast in the faith, knowing that the same afflictions are accomplished in your brethren that are in the world.”
King James Version (KJV)
You searched for
"ORGAN" in the KJV Bible
3 Instances - Page 1 of 1 - Sort by Book Order - Feedback
- Job 30:31chapter context similar meaning copy save
- My harp also is turned to mourning, and my organ into the voice of them that weep.
- Job 21:12chapter context similar meaning copy save
- They take the timbrel and harp, and rejoice at the sound of the organ.
- Genesis 4:21chapter context similar meaning copy save
- And his brother's name was Jubal: he was the father of all such as handle the harp and organ.
Organ (biology)
| Organ | |
|---|---|
 Many of the internal organs of the human body | |
| Details | |
| System | Organ systems |
| Identifiers | |
| Greek | Οργανο |
| FMA | 67498 |
| Anatomical terminology | |
In a multicellular organism, an organ is a collection of tissues joined in a structural unit to serve a common function.[1] In the hierarchy of life, an organ lies between tissue and an organ system. Tissues are formed from same type cells to act together in a function. Tissues of different types combine to form an organ which has a specific function. The intestinal wall for example is formed by epithelial tissue and smooth muscle tissue.[2] Two or more organs working together in the execution of a specific body function form an organ system, also called a biological system or body system.
An organ's tissues can be broadly categorized as parenchyma, the functional tissue, and stroma, the structural tissue with supportive, connective, or ancillary functions. For example, the gland's tissue that makes the hormones is the parenchyma, whereas the stroma includes the nerves that innervate the parenchyma, the blood vessels that oxygenate and nourish it and carry away its metabolic wastes, and the connective tissues that provide a suitable place for it to be situated and anchored. The main tissues that make up an organ tend to have common embryologic origins, such as arising from the same germ layer. Organs exist in most multicellular organisms. In single-celled organisms such as members of the eukaryotes, the functional analogue of an organ is known as an organelle. In plants, there are three main organs.[3]
The number of organs in any organism depends on the definition used. By one widely adopted definition, 79 organs have been identified in the human body.[4]
Animals[edit]
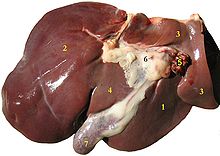
Except for placozoans, multicellular animals including humans have a variety of organ systems. These specific systems are widely studied in human anatomy. The functions of these organ systems often share significant overlap. For instance, the nervous and endocrine system both operate via a shared organ, the hypothalamus. For this reason, the two systems are combined and studied as the neuroendocrine system. The same is true for the musculoskeletal system because of the relationship between the muscular and skeletal systems.
- Cardiovascular system: pumping and channeling blood to and from the body and lungs with heart, blood and blood vessels.
- Digestive system: digestion and processing food with salivary glands, esophagus, stomach, liver, gallbladder, pancreas, intestines, colon, mesentery, rectum and anus.
- Endocrine system: communication within the body using hormones made by endocrine glands such as the hypothalamus, pituitary gland, pineal bodyor pineal gland, thyroid, parathyroids and adrenals, i.e., adrenal glands.
- Excretory system: kidneys, ureters, bladder and urethra involved in fluid balance, electrolyte balance and excretion of urine.
- Lymphatic system: structures involved in the transfer of lymph between tissues and the blood stream, the lymph and the nodes and vessels that transport it including the immune system: defending against disease-causing agents with leukocytes, tonsils, adenoids, thymus and spleen.
- Integumentary system: skin, hair and nails of mammals. Also scales of fish, reptiles, and birds, and feathers of birds.
- Muscular system: movement with muscles.
- Nervous system: collecting, transferring and processing information with brain, spinal cord and nerves.
- Reproductive system: the sex organs, such as ovaries, oviducts, uterus, vulva, vagina, testicles, vas deferens, seminal vesicles, prostate and penis.
- Respiratory system: the organs used for breathing, the pharynx, larynx, trachea, bronchi, lungs and diaphragm.
- Skeletal system: structural support and protection with bones, cartilage, ligaments and tendons.
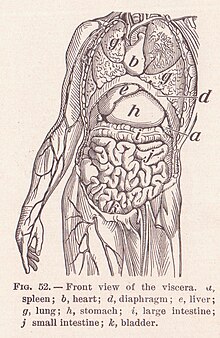
Viscera[edit]
In the study of anatomy, viscera (sg: viscus) refers to the internal organs of the abdominal, thoracic, and pelvic cavities.[5] The abdominal organs may be classified as solid organs or hollow organs. The solid organs are the liver, pancreas, spleen, kidneys, and adrenal glands. The hollow organs of the abdomen are the stomach, intestines, gallbladder, bladder, and rectum.[6] In the thoracic cavity, the heart is a hollow, muscular organ.[7] Splanchnology is the study of the viscera.[8] The term "visceral" is contrasted with the term "parietal", meaning "of or relating to the wall of a body part, organ or cavity".[9]The two terms are often used in describing a membrane or piece of connective tissue, referring to the opposing sides.[10]
Origin and evolution[edit]

The organ level of organisation in animals can be first detected in flatworms and the more derived phyla, i.e. the bilaterians. The less-advanced taxa (i.e. Placozoa, Porifera, Ctenophora and Cnidaria) do not show consolidation of their tissues into organs.
More complex animals are composed of different organs, which have evolved over time. For example, the liver and heart evolved in the chordates about 550-500 million years ago, while the gut and brain are even more ancient, arising in the ancestor of vertebrates, insects, molluscs, and worms about 700-650 million years ago.
Given the ancient origin of most vertebrate organs, researchers have looked for model systems, where organs have evolved more recently, and ideally have evolved multiple times independently. An outstanding model for this kind of research is the placenta, which has evolved more than 100 times independently in vertebrates, has evolved relatively recently in some lineages, and exists in intermediate forms in extant taxa.[11] Studies on the evolution of the placenta have identified a variety of genetic and physiological processes that contribute to the origin and evolution of organs, these include the re-purposing of existing animal tissues, the acquisition of new functional properties by these tissues, and novel interactions of distinct tissue types.[11]
Plants[edit]


The study of plant organs is covered in plant morphology. Organs of plants can be divided into vegetative and reproductive. Vegetative plant organs include roots, stems, and leaves. The reproductive organs are variable. In flowering plants, they are represented by the flower, seed and fruit.[citation needed] In conifers, the organ that bears the reproductive structures is called a cone. In other divisions (phyla) of plants, the reproductive organs are called strobili, in Lycopodiophyta, or simply gametophores in mosses. Common organ system designations in plants include the differentiation of shoot and root. All parts of the plant above ground (in non-epiphytes), including the functionally distinct leaf and flower organs, may be classified together as the shoot organ system.[12]
The vegetative organs are essential for maintaining the life of a plant. While there can be 11 organ systems in animals, there are far fewer in plants, where some perform the vital functions, such as photosynthesis, while the reproductive organs are essential in reproduction. However, if there is asexual vegetative reproduction, the vegetative organs are those that create the new generation of plants (see clonal colony).
Society and culture[edit]
Many societies have a system for organ donation, in which a living or deceased donor's organ are transplantedinto a person with a failing organ. The transplantation of larger solid organs often requires immunosuppression to prevent organ rejection or graft-versus-host disease.
There is considerable interest throughout the world in creating laboratory-grown or artificial organs.[citation needed]
Organ transplants[edit]
Beginning in the 20th century[13] organ transplants began to take place as scientists knew more about the anatomy of organs. These came later in time as procedures were often dangerous and difficult.[14] Both the source and method of obtaining the organ to transplant are major ethical issues to consider, and because organs as resources for transplant are always more limited than demand for them, various notions of justice, including distributive justice, are developed in the ethical analysis. This situation continues as long as transplantation relies upon organ donors rather than technological innovation, testing, and industrial manufacturing.[citation needed]
History[edit]
The English word "organ" dates back to the twelfth century and refers to any musical instrument. By the late 14th century, the musical term's meaning had narrowed to refer specifically to the keyboard-based instrument. At the same time, a second meaning arose, in reference to a "body part adapted to a certain function".[15]
Plant organs are made from tissue composed of different types of tissue. The three tissue types are ground, vascular, and dermal.[16] When three or more organs are present, it is called an organ system.[17]
The adjective visceral, also splanchnic, is used for anything pertaining to the internal organs. Historically, viscera of animals were examined by Roman pagan priests like the haruspices or the augurs in order to divine the future by their shape, dimensions or other factors.[18] This practice remains an important ritual in some remote, tribal societies.
The term "visceral" is contrasted with the term "parietal", meaning "of or relating to the wall of a body part, organ or cavity"[9] The two terms are often used in describing a membrane or piece of connective tissue, referring to the opposing sides.[19]
Antiquity[edit]
Aristotle used the word frequently in his philosophy, both to describe the organs of plants or animals (e.g. the roots of a tree, the heart or liver of an animal), and to describe more abstract "parts" of an interconnected whole (e.g. his logical works, taken as a whole, are referred to as the Organon).[20]
Some alchemists (e.g. Paracelsus) adopted the Hermetic Qabalah assignment between the seven vital organs and the seven classical planets as follows: [21]
| Planet | Organ |
|---|---|
| Sun | Heart |
| Moon | Brain |
| Mercury | Lungs |
| Venus | Kidneys |
| Mars | Gall bladder |
| Jupiter | Liver |
| Saturn | Spleen |
Chinese traditional medicine recognizes eleven organs, associated with the five Chinese traditional elements and with yin and yang, as follows:
| Element | Yin/yang | Organ |
|---|---|---|
| Wood | yin | liver |
| yang | gall bladder | |
| Fire | yin | heart |
| yang | small intestine / san jiao | |
| Earth | yin | spleen |
| yang | stomach | |
| Metal | yin | lungs |
| yang | large intestine | |
| Water | yin | kidneys |
| yang | bladder |
The Chinese associated the five elements with the five planets (Jupiter, Mars, Venus, Saturn, and Mercury) similar to the way the classical planets were associated with different metals. The yin and yang distinction approximates the modern notion of solid and hollow organs.
You searched for
"DIFFERENCE" in the KJV Bible
11 Instances - Page 1 of 1 - Sort by Book Order - Feedback
- Ezekiel 22:26chapter context similar meaning copy save
- Her priests have violated my law, and have profaned mine holy things: they have put no difference between the holy and profane, neither have they shewed difference between the unclean and the clean, and have hid their eyes from my sabbaths, and I am profaned among them.
- Jude 1:22chapter context similar meaning copy save
- And of some have compassion, making a difference:
- Acts 15:9chapter context similar meaning copy save
- And put no difference between us and them, purifying their hearts by faith.
- Romans 3:22chapter context similar meaning copy save
- Even the righteousness of God which is by faith of Jesus Christ unto all and upon all them that believe: for there is no difference:
- Leviticus 10:10chapter context similar meaning copy save
- And that ye may put difference between holy and unholy, and between unclean and clean;
- Romans 10:12chapter context similar meaning copy save
- For there is no difference between the Jew and the Greek: for the same Lord over all is rich unto all that call upon him.
- Ezekiel 44:23chapter context similar meaning copy save
- And they shall teach my people the difference between the holy and profane, and cause them to discern between the unclean and the clean.
- Exodus 11:7chapter context similar meaning copy save
- But against any of the children of Israel shall not a dog move his tongue, against man or beast: that ye may know how that the LORD doth put a difference between the Egyptians and Israel.
- Leviticus 20:25chapter context similar meaning copy save
- Ye shall therefore put difference between clean beasts and unclean, and between unclean fowls and clean: and ye shall not make your souls abominable by beast, or by fowl, or by any manner of living thing that creepeth on the ground, which I have separated from you as unclean.
- 1 Corinthians 7:34chapter context similar meaning copy save
- There is difference also between a wife and a virgin. The unmarried woman careth for the things of the Lord, that she may be holy both in body and in spirit: but she that is married careth for the things of the world, how she may please her husband.
- Leviticus 11:47chapter context similar meaning copy save
- To make a difference between the unclean and the clean, and between the beast that may be eaten and the beast that may not be eaten.
About Us
Contact - KPAX /Missoula or KAJ /Kalispell
Main Phone number: 406-542-4400
Mailing Address: 2204 Regent St, Missoula, MT 59801
News Director - Keith.Hatten@kpax.com
News Department - news@kpax.com
Director of Sales - Justin.Hartley@kpax.com
Digital Director – Shawna.Batt@kpax.com
Engineering - tech@kpax.com
Programming - Tonya.Robert@kpax.com
Production - James.Sanders@kpax.com
Station FCC Public File Contact: Lauri.Pulley@kpax.com













No comments:
Post a Comment