| Serotonin |
|---|
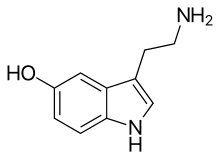 |
| IUPAC name | 3-(2-Aminoethyl)indol-5-ol |
|---|
| Synonyms | 5-Hydroxytryptamine, Enteramine; Thrombocytin, 3-(β-Aminoethyl)-5-hydroxyindole, Thrombotonin |
|---|
| Abbreviation | 5-HT |
|---|
| Sources | raphe nuclei, enterochromaffin cells |
|---|
| Targets | system-wide |
|---|
| Receptors | 5-HT1, 5-HT2, 5-HT3, 5-HT4, 5-HT5, 5-HT6, 5-HT7 |
|---|
| Agonists | SSRIs, MAOIs (indirectly) |
|---|
| Precursor | 5-HTP |
|---|
| Synthesizing enzyme | Aromatic L-amino acid decarboxylase |
|---|
| Metabolizing enzyme | MAO |
|---|
| Database links |
|---|
| CAS Number | 50-67-9  |
|---|
| PubChem | CID: 5202 |
|---|
| IUPHAR/BPS | 5 |
|---|
| ChemSpider | 5013  |
|---|
| KEGG | C00780  |
|---|
Serotonin |
 |
| Names |
|---|
| IUPAC names 5-Hydroxytryptamine or
3-(2-Aminoethyl)indol-5-ol |
| Other names 5-Hydroxytryptamine, 5-HT, Enteramine; Thrombocytin, 3-(β-Aminoethyl)-5-hydroxyindole, Thrombotonin |
| Identifiers |
|---|
| 50-67-9  |
| ChEBI | CHEBI:28790  |
| ChEMBL | ChEMBL39  |
| ChemSpider | 5013  |
| 5 |
| Jmol 3D model | Interactive image |
| KEGG | C00780  |
| MeSH | Serotonin |
| PubChem | 5202 |
| UNII | 333DO1RDJY  |
|
|
| Properties |
|---|
| C10H12N2O |
| Molar mass | 176.215 g/mol |
| Appearance | White powder |
| Melting point | 167.7 °C (333.9 °F; 440.8 K) 121–122 °C (ligroin)[3] |
| Boiling point | 416 ± 30 °C (at 760 Torr)[1] |
| slightly soluble |
| Acidity (pKa) | 10.16 in water at 23.5 °C[2] |
| 2.98 D |
| Hazards |
|---|
| Safety data sheet | External MSDS |
| Lethal dose or concentration (LD, LC): |
| 750 mg/kg (subcutaneous, rat),[4] 4500 mg/kg (intraperitoneal, rat),[5] 60 mg/kg (oral, rat) |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). |
 verify (what is verify (what is   ?) ?) |
| Infobox references |
| |
Approximately 90% of the
human body's total serotonin is located in the
enterochromaffin cells in the GI tract, where it is used to regulate intestinal movements.
[11][12] The serotonin is secreted
luminally and
basolaterally which leads to increased serotonin uptake by circulating platelets and activation after stimulation, which gives increased stimulation of myenteric neurons and
gastrointestinal motility.
[13] The remainder is synthesized in
serotonergic neurons of the CNS, where it has various functions. These include the regulation of
mood,
appetite, and
sleep. Serotonin also has some cognitive functions, including memory and learning. Modulation of serotonin at synapses is thought to be a major action of several classes of pharmacological antidepressants.
Serotonin secreted from the
enterochromaffin cells eventually finds its way out of tissues into the blood. There, it is actively taken up by blood
platelets, which store it. When the platelets bind to a clot, they release serotonin, where it serves as a
vasoconstrictor and helps to regulate
hemostasis and blood clotting. Serotonin also is a growth factor for some types of cells, which may give it a role in wound healing. There are various
serotonin receptors.
Serotonin is metabolized mainly to
5-HIAA, chiefly by the liver. Metabolism involves first
oxidation by
monoamine oxidase to the corresponding
aldehyde. This is followed by oxidation by
aldehyde dehydrogenase to 5-HIAA, the indole acetic acid derivative. The latter is then excreted by the kidneys. One type of tumor, called
carcinoid, sometimes secretes large amounts of serotonin into the blood, which causes various forms of the
carcinoid syndrome of
flushing (serotonin itself does not cause flushing). Potential causes of flushing in carcinoid syndrome include
bradykinins,
prostaglandins,
tachykinins,
substance P, and/or
histamine,
diarrhea, and heart problems. Because of serotonin's growth-promoting effect on
cardiac myocytes,
[14] a serotonin-secreting carcinoid tumour may cause a
tricuspid valve disease syndrome, due to the proliferation of
myocytes onto the valve.
[citation needed]In addition to
animals, serotonin is found in
fungi and
plants.
[15] Serotonin's presence in insect venoms and plant spines serves to cause pain, which is a side-effect of serotonin injection. Serotonin is produced by pathogenic amoebae, and its effect on the gut causes diarrhea. Its widespread presence in many seeds and fruits may serve to stimulate the digestive tract into expelling the seeds.
Functions[edit]
Serotonin is a neurotransmitter and is found in all
bilateral animals, where it mediates gut movements and the animal's perceptions of resource availability .
[citation needed] In less complex animals, such as some
invertebrates, resources simply mean food availability. In more complex animals, such as
arthropods and
vertebrates, resources also can mean social dominance. In response to the perceived abundance or scarcity of resources, an animal's growth, reproduction or
mood may be elevated or lowered. This may somewhat depend on how much serotonin the organism has at its disposal.
[16]Cellular effects[edit]
Receptors[edit]
Main article:
5-HT receptorTermination[edit]
Contrasting with the high-affinity SERT, the PMAT has been identified as a low-affinity transporter, with an apparent K
m of 114 micromoles/l for serotonin; approximately 230 times higher than that of SERT. However, the PMAT, despite its relatively low serotonergic affinity, has a considerably higher transport 'capacity' than SERT, "..resulting in roughly comparable uptake efficiencies to SERT in heterologous expression systems." The study also suggests some SSRIs, such as
fluoxetine and
sertraline anti-depressants, inhibit PMAT but at
IC50 values which surpass the therapeutic plasma concentrations by up to four orders of magnitude. Therefore, SSRI monotherapy is "ineffective" in PMAT inhibition. At present, no known pharmaceuticals are known to appreciably inhibit PMAT at normal therapeutic doses. The PMAT also suggestively transports dopamine and norepinephrine, albeit at K
m values even higher than that of 5-HT (330–15,000 μmoles/L).
Serotonylation[edit]
Main article:
SerotonylationSerotonin can also signal through a nonreceptor mechanism called serotonylation, in which serotonin modifies proteins.
[19] This process underlies serotonin's effects upon platelet-forming cells (
thrombocytes) in which it links to the modification of signaling enzymes called
GTPases that then trigger the release of vesicle contents by
exocytosis.
[20] A similar process underlies the pancreatic release of insulin.
[19]The effects of serotonin upon vascular smooth
muscle tone (this is the biological function from which serotonin originally got its name) depend upon the serotonylation of proteins involved in the contractile apparatus of muscle cells.
[21]Binding profile of serotonin| Receptor | Ki(nM)[22] | Receptor function[Note 1] |
|---|
| 5-HT1 receptor family signals via Gi/o inhibition of adenylyl cyclase. |
| 5-HT1A | 3.17 | Memory[vague] (agonists ↓); learning[vague] (agonists ↓); anxiety (agonists ↓); depression (agonists ↓); positive, negative, and cognitive symptoms of schizophrenia (partial agonists ↓); analgesia (agonists ↑); aggression (agonists ↓); dopamine release in the prefrontal cortex (agonists ↑); serotonin release and synthesis (agonists ↓) |
| 5-HT1B | 4.32 | Vasoconstriction (agonists ↑); aggression (agonists ↓); bone mass (↓). Serotonin autoreceptor. |
| 5-HT1D | 5.03 | Vasoconstriction (agonists ↑) |
| 5-HT1E | 7.53 | |
| 5-HT1F | 10 | |
| 5-HT2 receptor family signals via Gq activation of phospholipase C. |
| 5-HT2A | 11.55 | Psychedelia (agonists ↑; antagonists ↑); depression (agonists & antagonists ↓); anxiety (antagonists ↓); positive and negative symptoms of schizophrenia (antagonists ↓); norepinephrine release from the locus coeruleus (antagonists ↑); glutamate release in the prefrontal cortex |
| 5-HT2B | 8.71 | Cardiovascular functioning (agonists increase risk of pulmonary hypertension), empathy (via the spindle neurons or Von Economo neurons[23]) |
| 5-HT2C | 5.02 | Dopamine release into the mesocorticolimbic pathway (agonists ↓); acetylcholine release in the prefrontal cortex (agonists ↑); appetite (agonists ↓); antipsychotic effects (agonists ↑); antidepressant effects (agonists & antagonists ↑) |
| Other 5-HT receptors |
| 5-HT3 | ? | Emesis (agonists ↑); anxiolysis (antagonists ↑) |
| 5-HT4 | 125.89 | Movement of food across the GI tract (agonists ↑); memory & learning (agonists ↑); antidepressant effects (agonists ↑). Signalling via Gαs activation of adenylyl cyclase. |
| 5-HT5A | 251.2 | Memory consolidation.[24] Signals via Gi/o inhibition of adenylyl cyclase |
| 5-HT6 | 98.41 | Cognition (antagonists ↑); antidepressant effects (agonists & antagonists ↑). Gs signalling via activating adenylyl cyclase. |
| 5-HT7 | 8.11 | Cognition (antagonists ↑); antidepressant effects (antagonists ↑). Acts by Gs signalling via activating adenylyl cyclase. |
Nervous system[edit]
The neurons of the
Raphe nuclei are the principal source of 5-HT release in the brain.
[25] There are 7 or 8 raphe nuclei (some scientists chose to group the
nuclei raphes lineares into one nucleus), all of which are located along the midline of the
brainstem, and centered on the
reticular formation.
[26] Axons from the neurons of the raphe nuclei form a
neurotransmitter system reaching almost every part of the central nervous system. Axons of neurons in the lower raphe nuclei terminate in the
cerebellum and
spinal cord, while the axons of the higher nuclei spread out in the entire brain.
Microanatomy[edit]
Serotonin is released into the space between neurons (synapse), and diffuses over a relatively wide gap (>20 µm) to activate
5-HT receptors located on the
dendrites, cell bodies and
presynaptic terminals of adjacent neurons.
When humans smell food, dopamine is released to
increase the appetite. But, unlike in worms, serotonin does not increase anticipatory behaviour in humans; instead, the serotonin released while consuming activates
5-HT2C receptors on dopamine-producing cells. This halts their dopamine release, and thereby serotonin decreases appetite. Drugs that block 5-HT
2C receptors make the body unable to recognize when it is no longer hungry or otherwise in need of nutrients, and are associated with increased weight gain,
[27] especially in people with a low number of receptors.
[28] The expression of 5-HT
2C receptors in the
hippocampus follows a
diurnal rhythm,
[29] just as the serotonin release in the
ventromedial nucleus, which is characterised by a peak at morning when the motivation to eat is strongest.
[30]How much food an animal gets not only depends on food availability but also depends on the animal's ability to compete with others. This is especially true for
social animals, where the stronger individuals might steal food from the weaker (this is not to say some non-social animals do not concern themselves with the needs of others or steal food from others
[citation needed]). Thus, serotonin is not only involved in the perception of food availability but also involved in social rank.
In
macaques, alpha males have twice the level of serotonin released in the brain than subordinate males and females (as measured by the levels of 5-Hydroxyindoleacetic acid (5-HIAA) in the cerebro-spinal fluid). Dominance status and cerebro-serotonin levels appear to be positively correlated. When dominant males were removed from such groups, subordinate males begin competing for dominance. Once new dominance hierarchies were established, serotonin levels of the new dominant individuals also increased to double those in subordinate males and females. The reason why serotonin levels are only high in dominant males but not dominant females has not yet been established.
[31]In humans, levels of 5-HT
1A receptor activation in the brain show negative correlation with aggression,
[32] and a mutation in the gene that codes for the
5-HT2A receptor may double the risk of suicide for those with that genotype.
[33] Serotonin in the brain is not usually degraded after use, but is collected by serotonergic neurons by
serotonin transporters on their cell surfaces. Studies have revealed nearly 10% of total variance in anxiety-related personality depends on variations in the
description of where, when and how many serotonin transporters the neurons should deploy.
[34]Outside the nervous system[edit]
In the digestive tract (emetic)[edit]
If irritants are present in the food, the enterochromaffin cells release more serotonin to make the gut move faster, i.e., to cause diarrhea, so the gut is emptied of the noxious substance. If serotonin is released in the blood faster than the platelets can absorb it, the level of free serotonin in the blood is increased. This activates
5HT3 receptors in the
chemoreceptor trigger zone that stimulate
vomiting.
[35] The enterochromaffin cells not only react to bad food but are also very sensitive to
irradiation and
cancer chemotherapy. Drugs that
block 5HT3 are very effective in controlling the nausea and vomiting produced by cancer treatment, and are considered the gold standard for this purpose.
[36]Bone metabolism[edit]
In mice and humans, alterations in serotonin levels and signalling have been shown to regulate bone mass.
[37][38][39][40] Mice that lack brain serotonin have
osteopenia, while mice that lack gut serotonin have high bone density. In humans, increased blood serotonin levels have been shown to be significant negative predictor of low bone density. Serotonin can also be synthesized, albeit at very low levels, in the bone cells. It mediates its actions on bone cells using three different receptors. Through
5-HT1B receptors, it negatively regulates bone mass, while it does so positively through
5-HT2B receptors and
5-HT2C receptors. There is very delicate balance between physiological role of gut serotonin and its pathology. Increase in the extracellular content of serotonin results in a complex relay of signals in the osteoblasts culminating in FoxO1/ Creb and ATF4 dependent transcriptional events.
[41] These studies have opened a new area of research in bone metabolism that can be potentially harnessed to treat bone mass disorders.
[42]Organ development[edit]
Since serotonin signals resource availability it is not surprising that it affects organ development. Many human and animal studies have shown that nutrition in early life can influence, in adulthood, such things as body fatness, blood lipids, blood pressure, atherosclerosis, behavior, learning and longevity.
[43][44][45] Rodent experiment shows that early life exposure to SSRI:s makes persistent changes in the serotonergic transmission of the brain resulting in behavioral changes,
[46][47] which are reversed by treatment with antidepressants.
[48] By treating normal and
knockout mice lacking the serotonin transporter with fluoxetine scientists showed that normal emotional reactions in adulthood, like a short latency to escape foot shocks and inclination to explore new environments were dependent on active serotonin transporters during the neonatal period.
[49][50]Cardiovascular growth factor[edit]
Serotonin, in addition, evokes
endothelial nitric oxide synthase activation and stimulates, through a
5-HT1B receptor-mediated mechanism, the phosphorylation of p44/p42 mitogen-activated protein kinase activation in bovine aortic endothelial cell cultures.
[55] In blood, serotonin is collected from plasma by platelets, which store it. It is thus active wherever platelets bind in damaged tissue, as a vasoconstrictor to stop bleeding, and also as a fibrocyte mitotic (growth factor), to aid healing.
[56]Medical uses[edit]
![[icon]](https://upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/1/1c/Wiki_letter_w_cropped.svg/20px-Wiki_letter_w_cropped.svg.png) | This section is empty. You can help by adding to it. (October 2015) |
Pharmacology[edit]
Psychedelic drugs[edit]
Antidepressants[edit]
Main articles:
SSRI and
MAOICertain SSRI medications have been shown to lower serotonin levels below the baseline after chronic use, despite initial increases.
[62] The
5-HTTLPR gene codes for the number of serotonin transporters in the brain, with more serotonin transporters causing decreased duration and magnitude of serotonergic signaling.
[63] The
5-HTTLPR polymorphism (l/l)causing more serotonin transporters to be formed is also found to be more resilient against depression and anxiety.
[64][65]Serotonin syndrome[edit]
Extremely high levels of serotonin can cause a condition known as
serotonin syndrome, with toxic and potentially fatal effects. In practice, such toxic levels are essentially impossible to reach through an
overdose of a single antidepressant drug, but require a combination of serotonergic agents, such as an
SSRI with an
MAOI.
[66] The intensity of the symptoms of serotonin syndrome vary over a wide spectrum, and the milder forms are seen even at nontoxic levels.
[67]Antiemetics[edit]
As with fenfluramine, some of these drugs have been withdrawn from the market after groups taking them showed a statistical increase of one or more of the side effects described. An example is
pergolide. The drug was declining in use since it was reported in 2003 to be associated with cardiac fibrosis.
[70]Two independent studies published in the
New England Journal of Medicine in January 2007, implicated pergolide, along with
cabergoline, in causing
valvular heart disease.
[71][72]As a result of this, the
FDA removed pergolide from the U.S. market in March 2007.
[73] (Since cabergoline is not approved in the U.S. for Parkinson's Disease, but for hyperprolactinemia, the drug remains on the market. Treatment for hyperprolactinemia requires lower doses than that for Parkinson's Disease, diminishing the risk of valvular heart disease).
[74]Methyl-tryptamines and hallucinogens[edit]
For details on tryptamine neurotransmitters in humans, see
Trace amine.
Several plants contain serotonin together with a family of related
tryptamines that are
methylated at the
amino (NH
2) and
(OH) groups, are
N-oxides, or miss the OH group. These compounds do reach the brain, although some portion of them are metabolized by
monoamine oxidase enzymes (mainly
MAO-A) in the liver. Examples are plants from the
Anadenanthera genus that are used in the
hallucinogenic yopo snuff. These compounds are widely present in the leaves of many plants, and may serve as deterrents for animal ingestion. Serotonin occurs in several mushrooms of the genus
Panaeolus.
[75]Diseases and disorders[edit]
Genetically altered mice that lack TPH2 are normal when they are born. However, after three days, they appear to be smaller and weaker, and have softer skin than their siblings. In a
purebred strain, 50% of the mutants died during the first four weeks, but in a mixed strain, 90% survived. Normally, the mother
weans the litter after three weeks, but the mutant animals needed five weeks. After that, they caught up in growth and had normal mortality rates. Subtle changes in the
autonomic nervous system are present, but the most obvious difference from normal mice is the increased aggressiveness and impairment in maternal care of young.
[77] Despite the blood-brain barrier, the loss of serotonin production in the brain is partially compensated by intestinal serotonin. The behavioural changes become greatly enhanced if one crosses TPH1- with TPH2-lacking mice and gets animals that lack TPH entirely.
[78]In humans, defective signaling of serotonin in the brain may be the root cause of
sudden infant death syndrome (SIDS). Scientists from the European Molecular Biology Laboratory in Monterotondo, Italy
[79] genetically modified lab mice to produce low levels of the neurotransmitter serotonin. The results showed the mice suffered drops in heart rate and other symptoms of SIDS, and many of the animals died at an early age. Researchers now believe low levels of serotonin in the animals' brainstems, which controls heartbeat and breathing, may have caused sudden death.
[51] If neurons that make serotonin — serotonergic neurons — are abnormal in human infants, there is a risk of
sudden infant death syndrome (SIDS).
[80]Recent research conducted at
Rockefeller University shows, in both patients who suffer from depression as well as mice that model the disorder, levels of the
p11 protein are decreased. This protein is related to serotonin transmission within the brain.
[81]Depletion of serotonin is common between disorders such as obsessive-compulsive disorder, depression, and anxiety. However, Dr. Marazziti and his researchers at the University of Pisa in Italy found that depletion of serotonin also occurs in people who have recently fallen in love. This leads to the obsessive component associated with early stages of love.
[82]Consumption of an average amount of alcohol (0.8g/kg of body weight) has been shown to decrease tryptophan by about 25%, leading to a similar decrease in serotonin. The sexual and impulsive behavior resulting from an intoxicated state is at least partially an effect of the decrease in serotonin because serotonin regulates these behaviors.
[82]Comparative biology and evolution[edit]
Unicellular organisms[edit]
Serotonin is used by a variety of single-cell organisms for various purposes.
SSRIs have been found to be toxic to algae.
[83] The gastrointestinal parasite
Entamoeba histolyticasecretes serotonin, causing a sustained secretory diarrhea in some patients.
[84][85] Patients infected with
E. histolytica have been found to have highly elevated serum serotonin levels, which returned to normal following resolution of the infection.
[86] E. histolytica also responds to the presence of serotonin by becoming more virulent.
[87] This means serotonin secretion not only serves to increase the spread of enteamoebas by giving the host diarrhea but also serves to coordinate their behaviour according to their population density, a phenomenon known as
quorum sensing. Outside the gut of a host, there is nothing that the entoamoebas provoke to release serotonin, hence the serotonin concentration is very low. Low serotonin signals to the entoamoebas they are outside a host and they become less virulent to conserve energy. When they enter a new host, they multiply in the gut, and become more virulent as the enterochromaffine cells get provoked by them and the serotonin concentration increases.
However, since serotonin is a major gastrointestinal tract modulator, it may be produced by plants in fruits as a way of speeding the passage of seeds through the digestive tract, in the same way as many well-known seed and fruit associated laxatives. Serotonin is found in
mushrooms,
fruits and
vegetables. The highest values of 25–400 mg/kg have been found in nuts of the
walnut (
Juglans) and
hickory (
Carya) genera. Serotonin concentrations of 3–30 mg/kg have been found in
plantains,
pineapples,
banana,
kiwifruit,
plums, and
tomatoes. Moderate levels from 0.1–3 mg/kg have been found in a wide range of tested vegetables.
[89]Serotonin is one compound of the poison contained in
stinging nettles (
Urtica dioica), where it causes pain on injection in the same manner as its presence in insect venoms (see below). It is also naturally found in
Paramuricea clavata, or the Red Sea Fan.
[90]Serotonin and tryptophan have been found in chocolate with varying cocoa contents. The highest serotonin content (2.93 µg/g) was found in chocolate with 85% cocoa, and the highest tryptophan content (13.27–13.34 µg/g) was found in 70–85% cocoa. The intermediate in the synthesis from tryptophan to serotonin, 5-hydroxytryptophan, was not found.
[91]Invertebrates[edit]
Serotonin functions as a neurotransmitter in the nervous systems of simple, as well as complex, animals. For example, in the roundworm
Caenorhabditis elegans, which feeds on bacteria, serotonin is released as a signal in response to positive events, e.g., finding a new source of food or in male animals finding a female with which to mate.
[92] When a well-fed worm feels bacteria on its
cuticle,
dopamine is released, which slows it down; if it is starved, serotonin also is released, which slows the animal down further. This mechanism increases the amount of time animals spend in the presence of food.
[93] The released serotonin activates the muscles used for feeding, while
octopamine suppresses them.
[94] Serotonin diffuses to serotonin-sensitive neurons, which control the animal's perception of nutrient availability.
Insects[edit]
Serotonin is evolutionary conserved and appears across the animal kingdom. It is seen in insect processes in roles similar to in the human central nervous system, such as memory, appetite, sleep, and behavior.
[97] Locust swarming is mediated by serotonin, by transforming social preference from aversion to a gregarious state that enables coherent groups.
[98] Learning in flies and honeybees is affected by the presence of serotonin.
[99][100] Insect 5-HT receptors have similar sequences to the vertebrate versions, but pharmacological differences have been seen. Invertebrate drug response has been far less characterized than mammalian pharmacology and the potential for species selective insecticides has been discussed.
[101]If flies are fed serotonin, they are more aggressive; flies depleted of serotonin still exhibit aggression, but they do so much less frequently.
[104]Growth and reproduction[edit]
In the nematode
C. elegans, artificial depletion of serotonin or the increase of octopamine cues behavior typical of a low-food environment:
C. elegans becomes more active, and mating and egg-laying are suppressed, while the opposite occurs if serotonin is increased or octopamine is decreased in this animal.
[105] Serotonin is necessary for normal nematode male mating behavior,
[106] and the inclination to leave food to search for a mate.
[107] The serotonergic signaling used to adapt the worm's behaviour to fast changes in the environment affects
insulin-like signaling and the
TGF beta signaling pathway,
[108] which control long-term adaption.
In the
fruit fly insulin both regulates
blood sugar as well as acting as a
growth factor. Thus in the fruit fly, serotonergic neurons regulate the adult body size by affecting insulin secretion.
[109][110] Serotonin has also been identified as the trigger for
swarm behavior in locusts.
[111] In humans, though insulin regulates blood sugar and
IGF regulates growth, serotonin controls the release of both hormones, modulating insulin release from the
beta cells in the
pancreas through serotonylation of GTPase signaling proteins.
[19] Exposure to
SSRIs during
Pregnancy reduces fetal growth.
[112]Aging and age-related phenotypes[edit]
Serotonin is known to regulate aging, learning and memory. The first evidence comes from the study of longevity in
C. elegans.
[113] During early phase of aging, the level of serotonin increases, which alters locomotory behaviors and associative memory.
[114] The effect is restored by mutations and drugs (including
mianserin and
methiothepin) that inhibit
serotonin receptors. The observation does not contradict with the notion that the serotonin level goes down in mammals and humans, which is typically seen in late but not early phase of aging.
Deficiency[edit]
Genetically altered
C. elegans worms that lack serotonin have an increased reproductive lifespan, may become obese, and sometimes present with arrested development at a
dormant larval state.
[115][116]Biochemical mechanisms[edit]
Biosynthesis[edit]

The pathway for the synthesis of serotonin from tryptophan.
Serotonin can be synthesized from tryptophan in the lab using
Aspergillus niger and
Psilocybe coprophila as catalysts. The first phase to 5-hydroxytryptophan would require letting tryptophan sit in ethanol and water for 7 days, then mixing in enough HCl (or other acid) to bring the pH to 3, and then adding NaOH to make a pH of 13 for 1 hour.
Asperigillus niger would be the catalyst for this first phase. The second phase to synthesizing tryptophan itself from the 5-hydroxytryptophan intermediate would require adding ethanol and water, and letting sit for 30 days this time. The next two steps would be the same as the first phase: adding HCl to make the pH = 3, and then adding NaOH to make the pH very basic at 13 for 1 hour. This phase uses the
Psilocybe coprophila as the catalyst for the reaction.
[117]Serotonin taken orally does not pass into the serotonergic pathways of the central nervous system, because it does not cross the
blood–brain barrier.
[118] However,
tryptophan and its
metabolite 5-hydroxytryptophan (5-HTP), from which serotonin is synthesized, does cross the blood–brain barrier. These agents are available as
dietary supplements, and may be effective serotonergic agents. One product of serotonin breakdown is
5-hydroxyindoleacetic acid (5-HIAA), which is excreted in the
urine. Serotonin and 5-HIAA are sometimes produced in excess amounts by certain
tumors or
cancers, and levels of these substances may be measured in the urine to test for these tumors.
Effects of food content[edit]
Consuming purified tryptophan increases brain serotonin whereas eating foods containing tryptophan does not.
[119]This is because the transport system which brings tryptophan across the
blood-brain barrier is also selective for the other amino acids contained in protein sources.
[118] High plasma levels of other large neutral amino acids compete for transport and prevent the elevated plasma tryptophan from increasing serotonin synthesis.
History[edit]
In 1952, enteramine was shown to be the same substance as serotonin, and as the broad range of physiological roles was elucidated, the abbreviation 5-HT of the proper chemical name 5-hydroxytryptamine became the preferred name in the pharmacological field.
[122] Synonyms of serotonin include: 5-hydroxytriptamine, thrombotin, enteramin, substance DS, and 3-(β-Aminoethyl)-5-hydroxyindole.
[123] In 1953,
Betty Twarog and Page discovered serotonin in the central nervous system.
[124]















No comments:
Post a Comment